
In this case, most individuals die early in life, as they are eaten by predators.Īnother way of analyzing the age distribution of a population is to construct an age pyramid, which shows the proportion of the population in each cohort. Now look at the second curve, based on a population of trout in a creek. This shape of curve is typical for animals that receive care during their lifetimes, indicating that most deaths are caused by old age. The curve for the sheep drops slowly until later in life. You can see that about half the sheep are expected to survive for 7 years The data shown here are for female domestic sheep. Life tables include data about the birth and deaths of cohorts, groups of individuals in a population that are the same age.ĭata from a life table are often used to plot a survivorship curve. Scientists construct life tables to determine the length of time that individuals in a population are expected to survive. For example, an elephant reproduces every 12 to 30 years, whereas a bacterium can reproduce three times in a single hour. Larger organisms usually have longer generation times. In general, this time is related to the size of the organism. The average time from the birth of an individual to the birth of its offspring is called the generation time. Most populations have overlapping generations. If there are many young organisms, the birth rate is high and the population will grow. If there are no young organisms and the population consists mainly of old organisms past their reproductive age, then the population is destined for extinction. In order to fully study the population's demographics, its statistical characteristics, we also need to know the distribution of ages.

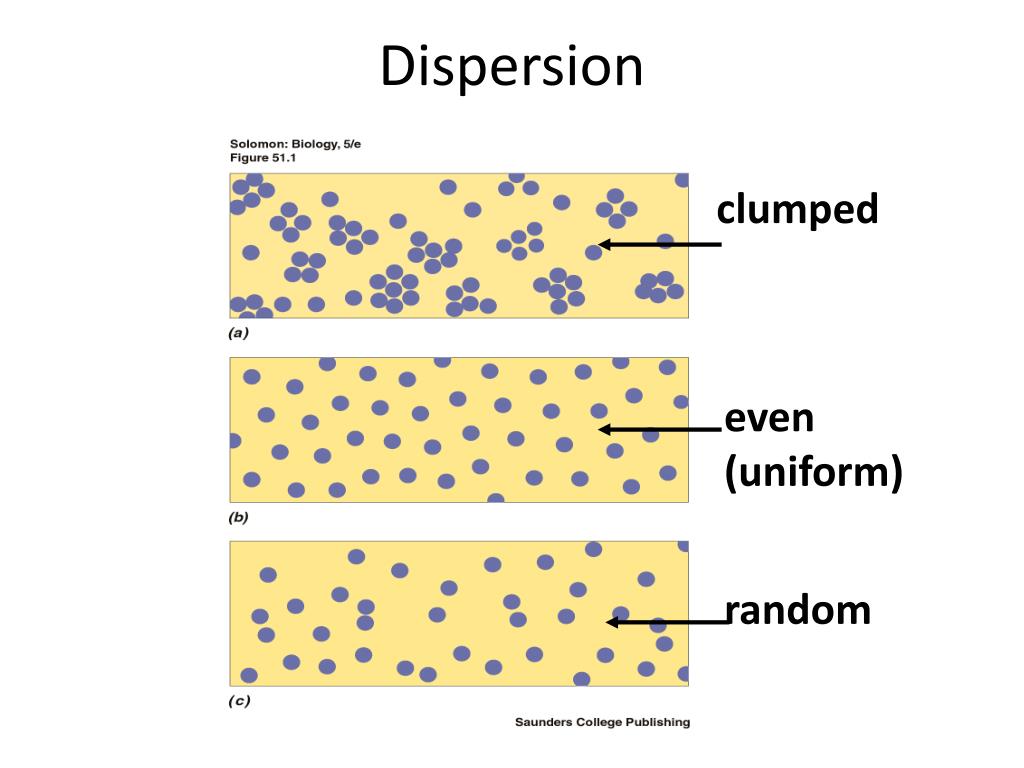
Population density gives information about population size. In a population, the number of individuals per unit area is called the population density. If birds or the wind scatter weed seeds on a lawn, any part of the lawn is fair game for the weeds, resulting in a random spatial pattern. Random distributions are found where these kind of factors don’t exist. The bushes are spaced far enough apart that they don’t compete for scarce resources. Clumped distribution may also be caused by the availability of food.Ī uniform distribution, as in the creosote bush population, results from competition for nutrients and water. The distribution of weeds in a lawn is much more haphazard, and this type of distribution is called a random distribution.Ī clumped distribution may be caused by behavioral factors.įor example, the bison group together for protection and to form families. The bison have a clumped distribution, whereas the creosote bushes have a uniform distribution. In contrast to the creosote bushes in the desert, each bison doesn’t graze at exactly the same distance from its neighbors, and the bison don’t completely fill the grassland valleys on which they graze. If we looked at the spacing among individuals in our herd of bison, we’d notice that the animals are pretty much grouped together. Data can be analyzed in a simple fashion or via advanced mixed models.Hippocampus Biology: Population Distribution Relatively sophisticated students could test whether parasites have a random dispersion pattern by comparing the histogram they generate to that of a Poisson distribution. Significant quantities of data can be generated in relatively short order and pooled for a class many patterns can emerge that challenge students to find logical interpretations. I describe one way to randomly sample leaves to quantify dispersion of such parasites and test whether dispersion is related to a variety of explanatory variables. Fungi are commonly observed parasites on leaves of trees. Accordingly, many researchers, including ecologists and medical practitioners, study dispersion of parasites in detail. The way in which parasites are distributed among hosts (their dispersion) can have profound importance for how they and their hosts coevolve, and for many other facets of their biology. Symbioses can range from mutualisms to parasitisms the latter are the foci of this exercise.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
